NECO Chemistry Essay And Obj Answers 2025 Scheduled for today 9th July, 2025
NECO Chemistry Essay And Obj Answers 2025
CHEMISTRY OBJ
01-10: CEDADDACEC
11-20: ECBAEBAEBD
21-30: BCBDECBCAE
31-40: CDDCBBCDED
41-50: DEAAADDABD
51-60: DBCEECDDED
COMPLETED
==============
(1ai)
Fermentation is the chemical breakdown of organic substances, especially sugars, by enzymes produced by microorganisms such as yeast, resulting in simpler compounds like alcohol, acids, and gases under anaerobic conditions.
(1aii)
(i) Hydrolysis of starch to glucose:
(C₆H₁₀O₅)ₙ + nH₂O ->> nC₆H₁₂O₆
(ii) Fermentation of glucose to ethanol:
C₆H₁₂O₆ ->> 2C₂H₅OH + 2CO₂
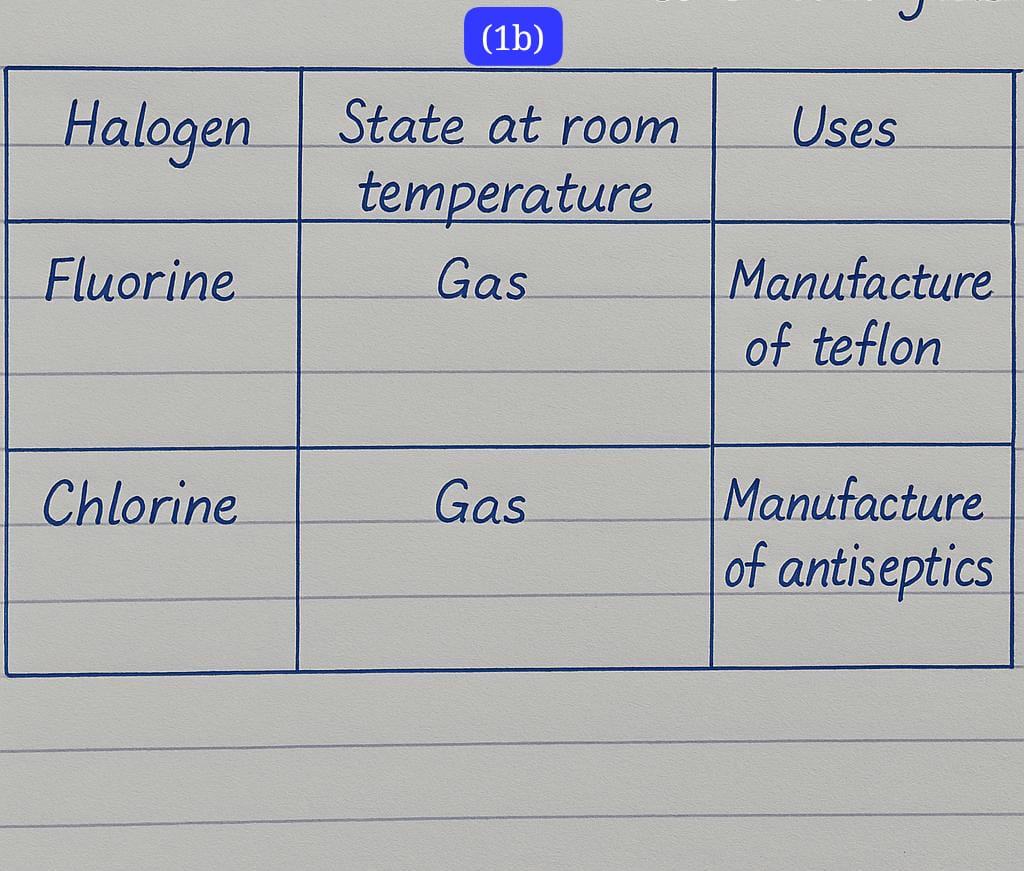
(1b)
check the image below
(1ci)
Molar mass of MgCO₃ = 24 + 12 + (16 × 3) = 84 g/mol
Moles = Mass / Molar Mass = 25 / 84 = 0.299 moles
(1cii)
Methyl orange
(1ciii)
=Acidic oxides=
(i) Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
(ii) Sulphur dioxide (SO₂)
(iii) Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂)
(iv) Phosphorus pentoxide (P₂O₅)
=Neutral oxides=
(i) Nitrous oxide (N₂O)
(ii) Carbon monoxide (CO)
(iii) Water (H₂O)
(iv) Nitric oxide (NO)
(1civ)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Hydrophobic compounds do not dissolve in water, while hydrophilic compounds dissolve easily in water.
(ii) Hydrophobic compounds repel water molecules, while hydrophilic compounds attract water molecules.
(iii) Hydrophobic compounds are usually non-polar, while hydrophilic compounds are often polar.
(iv) Hydrophobic compounds tend to cluster together in water, while hydrophilic compounds disperse evenly.
(v) Hydrophobic compounds are soluble in organic solvents, while hydrophilic compounds are soluble in aqueous solvents.
(1v)
(i) CH₃CH₂COOH ->> Propanoic acid
(ii) CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH ->> Butan-1-ol
(1di)
The rate of a chemical reaction is the speed at which reactants are converted into products, usually measured by the change in concentration of a substance per unit time.
(1dii)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Temperature
(ii) Concentration of reactants
(iii) Presence of a catalyst
(iv) Surface area of reactants
(v) Pressure (for gases)
(vi) Light (for photochemical reactions)
(vii) Nature of reactants
(viii) Stirring or agitation
==========
*NECO CHEMISTRY ANSWERS*
*NUMBER TWO*
(2ai)
An acid anhydride is a compound formed by the removal of water (H₂O) from two molecules of an acid. It reacts with water to form an acid.
(2aii)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH)
(ii) Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)
(iii) Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
(iv) Phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄)
(v) Nitrous acid (HNO₂)
(vi) Sulphurous acid (H₂SO₃)
(2aiii)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Fats are solid at room temperature, while oils are liquid at room temperature.
(ii) Fats are mostly found in animals, while oils are mostly obtained from plants.
(iii) Fats contain more saturated fatty acids, while oils contain more unsaturated fatty acids.
(iv) Oils tend to have lower melting points than fats.
(v) Fats are generally more stable and less prone to oxidation than oils.
(2bi)
check the image below
(2bii)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) It is a colourless gas.
(ii) It has a faint sweet smell.
(iii) It is slightly soluble in water.
(iv) It is less dense than air.
(v) It is highly flammable.
(vi) It burns with a sooty (luminous) flame in air.
(2biii)
Molar mass of H₂SO₄ = (2×1) + 32 + (4×16) = 98 g/mol
Moles of H₂SO₄ = 3.5 / 98 = 0.0357 mol
Molarity (M) = moles / volume ->> volume = moles / molarity
Volume = 0.0357 / 0.25
= 0.143 dm³ or 143 cm³
(2ci)
The periodic law states that the chemical and physical properties of elements repeat at regular intervals when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
(2cii)
check the image below
(2ciii)
(i) 17D
(ii) 3A and 13C
(2civ)
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Carbon black
(ii) Charcoal
(iii) Lampblack
(iv) Coke
(v) Soot
============
(3ai)
Entropy is a thermodynamic quantity that measures the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. It represents the amount of energy in a system that is unavailable to do useful work.
(3aii)
Volume of oxygen = 0.28 dm³
Mass = 0.4 g
Molar volume at s.t.p. = 22.4 dm³
Vapour density = (Molar mass / 2) = (Mass × 22.4) / (2 × Volume)
First, find molar mass:
Molar mass = (0.4 × 22.4) / 0.28 = 32 g/mol
Vapour density = 32 / 2
= 16
(3bi)
I:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Increase in temperature
(ii) Increase in pressure
(iii) Use of a suitable catalyst
(iv) Removal of product (NO) as it is formed
(v) Increasing the concentration of the reactants (N₂ or O₂)
II:
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) The reaction is endothermic (ΔH > 0), so increasing temperature favours product formation.
(ii) Increasing pressure shifts equilibrium towards fewer gas molecules, but here, molecules are equal so pressure has limited effect.
(iii) A catalyst speeds up the rate without affecting equilibrium position.
(iv) Removing product (NO) shifts equilibrium to the right, increasing yield.
(v) Increasing reactant concentration increases the forward reaction rate.
(3bii)
(i) Tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid (H₂SO₄)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Used in car batteries
(ii) Used in the manufacture of fertilizers
(iii) Used in the production of detergents
(iv) Used in petroleum refining
(v) Used in the manufacture of explosives
(vi) Used in dye and paint production
(ii) Diamond
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Used in cutting tools
(ii) Used in jewelry
(iii) Used in drilling bits for oil and gas
(iv) Used in engraving glass
(v) Used in high-precision scientific instruments
(vi) Used in thermal conductivity applications (heat sinks)
(iii) Carbon (IV) oxide (CO₂)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Used in fire extinguishers
(ii) Used in carbonated drinks
(iii) Used in photosynthesis by plants
(iv) Used as a refrigerant in cooling systems
(v) Used to create inert atmospheres in welding
(vi) Used in dry ice for preservation and cooling
(3biii)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Sodium chloride (NaCl)
(ii) Potassium nitrate (KNO₃)
(iii) Calcium sulphate (CaSO₄)
(iv) Magnesium chloride (MgCl₂)
(v) Ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl)
(vi) Zinc sulphate (ZnSO₄)
(3ci)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) It is a colourless liquid.
(ii) It has a characteristic aromatic (sweet) smell.
(iii) It is volatile (evaporates easily).
(iv) It is immiscible with water but dissolves in organic solvents.
(v) It has a boiling point of about 80°C.
(vi) It is flammable and burns with a sooty flame.
(3cii)
2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol
(3ciii)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Use of stabilizers or preservatives
(ii) Storing chemicals in airtight, cool containers
(iii) Avoid exposure to light and moisture
(iv) Use of protective coatings or packaging
(v) Store in non-reactive or suitable containers
(vi) Control of temperature and pH during storage
(3civ)
Graphite
(3di)
The basicity of ethanoic acid refers to the number of replaceable hydrogen ions (H⁺) present in one molecule of the acid during a reaction with a base
(3dii)
(i) Strong Electrolytes
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Sodium chloride (NaCl)
(ii) Sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄)
(iii) Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
(iv) Nitric acid (HNO₃)
(v) Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
(ii) Weak Electrolytes
(PICK ANY ONE)
(i) Ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH)
(ii) Ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH)
(iii) Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)
(iv) Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
(v) Water (H₂O)
===============

Kolade Kayode, known as Mr. KK, I am a Nigerian education blogger and founder of MasterWAEC.com. Passionate about student success, I simplifies WAEC exam preparation with accurate tips and resources to help students excel.
